Minimum Wages in West Bengal: If you’re working in West Bengal or planning to start a business there, it’s crucial to understand the minimum wage laws in the state. In this article, we’ll delve into the nitty-gritty of minimum wages in West Bengal, covering everything from the legal framework to the current rates.
Table of Contents
The Minimum Wages Act of 1948
The Minimum Wages Act of 1948 is the central legislation that governs minimum wages in India, including West Bengal. The act was enacted to ensure that workers receive a minimum wage for their work and to prevent employers from exploiting workers by paying them very low wages.
Under the act, the state government is responsible for enforcing the minimum wage rates and ensuring that employers comply with the mandated rates. The state government sets minimum wage rates for different types of work and industries based on factors such as the cost of living, inflation, and industry norms.
In West Bengal, the minimum wage rates are revised periodically, and the state government publishes updated rates on its official website. The minimum wage rates in West Bengal vary based on the type of work and industry. For example, the minimum wage for unskilled agricultural workers is INR 322 per day, while the minimum wage for skilled workers in the electricity sector is INR 619 per day.
The Minimum Wages Act also sets penalties for employers who fail to pay their workers the mandated minimum wages. Employers who violate the act can face legal action, including fines and imprisonment. Workers who are not paid the minimum wages can file a complaint with the labor department, which can investigate and take action against the employer.
The act also provides for the establishment of advisory boards, which are responsible for advising the state government on matters related to minimum wages. The advisory boards comprise representatives of employers, workers, and independent experts, and they meet periodically to discuss and recommend changes to the minimum wage rates.
In conclusion, the Minimum Wages Act of 1948 is a crucial legislation that governs minimum wages in West Bengal and other states in India. The act protects workers from being exploited by employers who may otherwise pay them very low wages and ensures that workers receive a fair wage for their work. The state government must enforce the act and set minimum wage rates that are reasonable and fair to workers.
Salient Features of the Minimum Wages Act
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To ensure that workers receive a minimum wage for their work and to prevent employers from exploiting workers by paying them very low wages. |
| Applicability | Applies to all employees engaged in scheduled or unscheduled employment in West Bengal. |
| Minimum wage rates | The state government sets minimum wage rates for different types of work and industries based on factors such as the cost of living, inflation, and industry norms. |
| Revision of rates | The minimum wage rates are revised periodically, and the state government publishes updated rates on its official website. |
| Penalty for non-compliance | Employers who fail to pay their workers the mandated minimum wages can face legal action, including fines and imprisonment. |
| Establishment of advisory boards | Advisory boards, comprising representatives of employers, workers, and independent experts, are established to advise the state government on matters related to minimum wages. |
| Powers of inspectors | Inspectors appointed under the act have the power to enter any establishment covered under the act and inspect records, registers, and notices relating to minimum wages. |
| Complaints mechanism | Workers who are not paid the minimum wages can file a complaint with the labor department, which can investigate and take action against the employer. |
| Maintenance of records | Employers covered under the act are required to maintain registers and records related to minimum wages and make them available for inspection by labor department officials. |
| Non-retroactivity | The act does not affect any right or privilege that an employee was entitled to before the act came into force. |
What are Minimum Wages?
Minimum wages are the minimum amount of money that an employer must pay to their employees for a specific type of work, as mandated by the government. The rationale behind minimum wages is to protect workers from being exploited by employers who may otherwise pay them very low wages.
Current Minimum Wages in West Bengal
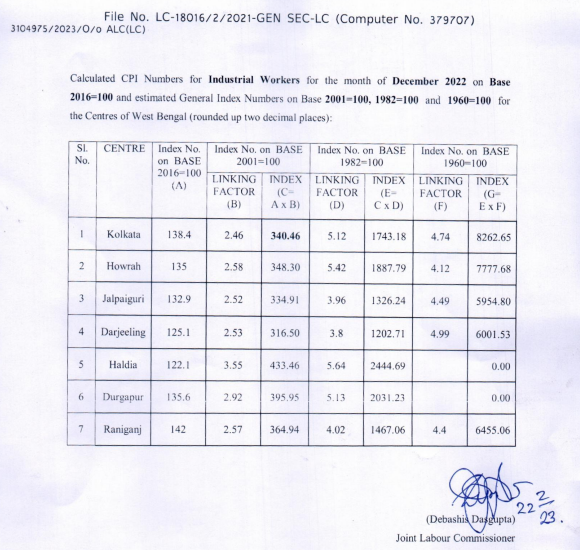
Legal Framework of Minimum Wages in West Bengal
The Minimum Wages Act of 1948 is the central legislation that governs the minimum wages in India, including West Bengal. The Act is enforced by the state government, which sets the minimum wage rates for different types of work and industries. The rates are revised periodically, based on the cost of living, inflation, and other factors.
Types of Minimum Wages in West Bengal
There are two types of minimum wages in West Bengal:
- Scheduled Employment: This refers to work that is covered under the Schedule of Employment under the Minimum Wages Act. The Schedule covers various types of work, such as mining, construction, agriculture, and more.
- Unscheduled Employment: This refers to work that is not covered under the Schedule of Employment. However, the state government may still prescribe minimum wages for such work based on factors such as skill level, experience, and industry norms.
Current Minimum Wages in West Bengal
The current minimum wage rates in West Bengal (as of January 2023) are as follows:
- Scheduled Employment: The minimum wage rates vary based on the type of work and industry. For example, the minimum wage for unskilled agricultural workers is INR 322 per day, while the minimum wage for skilled workers in the electricity sector is INR 619 per day.
- Unscheduled Employment: The minimum wage rates for unscheduled employment vary based on the skill level and industry. For example, the minimum wage for unskilled workers in the construction industry is INR 396 per day, while the minimum wage for semi-skilled workers in the hotel industry is INR 528 per day.
Legal Issue of Non-compliance of Minimum Wages of West Bengal
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Employers who fail to pay their workers the mandated minimum wages can face legal action, including fines and imprisonment. Workers who are not paid the minimum wages can file a complaint with the labor department, which can investigate and take action against the employer.
Minimum wages are an important aspect of labor laws in West Bengal, and employers must comply with the mandated rates to avoid legal consequences. Workers must also be aware of their rights and raise their voice against any employer who fails to pay the minimum wages. We hope this article has provided a comprehensive guide to minimum wages in West Bengal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Minimum Wages in West Bengal
- What are minimum wages in West Bengal? Minimum wages in West Bengal refer to the minimum amount of money that employers must pay to their employees for a specific type of work, as mandated by the government. The rates are determined by the state government and are revised periodically.
- What is the legal framework for minimum wages in West Bengal? The Minimum Wages Act of 1948 is the central legislation that governs minimum wages in India, including West Bengal. The state government is responsible for enforcing the act and setting minimum wage rates for different types of work and industries.
- What types of employment are covered under minimum wage laws in West Bengal? There are two types of employment covered under minimum wage laws in West Bengal: scheduled employment and unscheduled employment. Scheduled employment refers to work that is covered under the Schedule of Employment under the Minimum Wages Act, while unscheduled employment refers to work that is not covered under the Schedule of Employment.
- What is the current minimum wage rate in West Bengal? The current minimum wage rates in West Bengal (as of January 2023) vary based on the type of work and industry. For example, the minimum wage for unskilled agricultural workers is INR 322 per day, while the minimum wage for skilled workers in the electricity sector is INR 619 per day.
- What happens if an employer fails to pay the mandated minimum wages? Employers who fail to pay their workers the mandated minimum wages can face legal action, including fines and imprisonment. Workers who are not paid the minimum wages can file a complaint with the labor department, which can investigate and take action against the employer.
- How often are the minimum wage rates revised in West Bengal? The minimum wage rates in West Bengal are revised periodically based on the cost of living, inflation, and other factors. The state government typically revises the rates once every few years.
- Can an employer pay their employees more than the minimum wage rates? Yes, an employer can pay their employees more than the minimum wage rates. However, they must still pay at least the mandated minimum wage rate for the specific type of work and industry.
- How can workers raise their voice against employers who fail to pay the minimum wages? Workers who are not paid the minimum wages can file a complaint with the labor department, which can investigate and take action against the employer. They can also seek legal assistance to fight for their rights.
| Go To Sundarban News Today’s Home Page | Click Here |
| Go To West Bengal Government Site | Click Here |
| Article Category | West Bengal Scheme |

